by Antonio Donnangelo
Share

Introduction
The following article aims to summarize two important opportunities for the development of the agricultural sector:
The Agriculture Innovation Fund and the
ACA 24 – SRA24. Both are aimed at the dissemination of tools and technologies to
foster agricultural innovation projects
and improve the use of resources.
Agriculture Innovation Fund
The Agriculture Innovation Fund was established by Budget Law 2023 (Art. 1, paragraphs 428 et seq. of L.197/2022) with the aim of promote innovation projects aimed at improving productivity in the agriculture, fisheries and aquaculture sectors. This innovation support is based on the dissemination of technologies for the digital management of agricultural enterprises, the use of machines, robotic solutions, sensors, platforms and infrastructure 4.0, the promotion of water saving and the reduction of chemical use.
To whom it is addressed:
The beneficiaries of this fund are individual or associated small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), including their cooperatives and associations, which are registered as “agricultural enterprise,” “fishing enterprise,” or “agro-mechanical enterprise” in the Register of Enterprises, have their operational headquarters in Italy, and have been active for at least two years at the time of application submission. In addition, they must make investments in technological innovation between 70,000 euros and 500,000 euros, while for the fishing sector the minimum investment limit is set at 10,000 euros.
What the fund consists of:
The Agricultural Innovation Fund finances the purchase of:
- Agricultural machinery, drones, tools and equipment;
- machinery for animal husbandry;
- Agricultural tractors with Stage V engines.
The specifications for each type of investment are defined in the announcement. Fundable items must be brand new and must be tied to the recipient’s business for at least five years.
Magnitude of the fund:
The Agriculture Innovation Fund makes available.
75 million for each of the years 2023, 2024 and 2025.
The support takes the form of a
non-repayable grant
the amount of which varies depending on the sector in which the SMEs operate and the amount of eligible expenses.
The subsidy is calculated by applying the percentages established by the Ministerial Decree of Aug. 9, 2023, published in O.J. No. 240 of October 13, 2023, which vary 45% to 100% of eligible expenses.
Mode of delivery:
Disbursement of the non-repayable grant takes place in one lump sum. Alternatively, the beneficiary may arrange for the payment of the grant to be made, on its own behalf, by ISMEA directly to the supplier.
Submission of application:
The SME wishing to access the facilities submits the relevant application, using the forms made available by ISMEA on the dedicated portal. Applications for facilities are processed by ISMEA in chronological order of submission.
ACA 24 – SRA 24 Precision agriculture practices.
Objectives:
The purpose of the intervention is to Contribute to climate change mitigation and adaptive capacity, including by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving carbon sequestration, and to promote efficient use of natural resources such as water, soil and air.
ACA 24 currently has been included within supports from 9 Italian regions: Basilicata, Calabria, Campania, Lazio, Liguria, Piedmont, Apulia, Tuscany and Umbria.
What the support consists of:
ACA 24 provides for un annual per hectare support for farmers who commit to at least one precision agriculture practice such as the use of satellite imagery and from drones, predictive models, DSS, GNSS systems on tractors, VRT variable rate farming machines, IOT sensing, etc…, to improve production efficiency and reduce pesticide inputs.
Implementation:
The intervention consists of 3 actions that can also be taken simultaneously on the same surface:
Action 1:
Adoption of precision techniques –
Fertilizations
- Action 2: Adoption of precision techniques – Phytosanitary treatments
- Action 3: Adoption of precision techniques – Irrigations
Type of support:
Support is an annual payment granted per agricultural area under commitment with varying amounts for actions and crop groups.
Who can apply for aid and minimum areas:
Beneficiaries are:
- farmers, individual or associated;
- Public bodies managing farms.
Herbaceous, horticultural and tree crops are allowed.
For Tuscany, the minimum area under commitment is 3 hectares for herbaceous crops and 1 hectare for horticultural and tree crops. The areas for which the premium is claimed must fall within the regional territory.
Rewards:
Support consists of the
disbursement of an annual premium per hectare of agricultural area affected by one or more precision agriculture actions, including on the same area.
The premium per hectare is differentiated by Actions (1, 2 and 3) and crop groups (grasses, vegetables and trees) (Tab. 1).
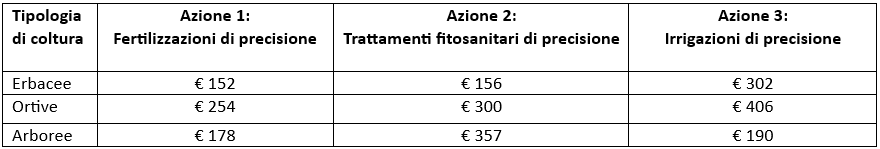
Tab.1: Premium amounts per hectare by type of action and crop group for the Tuscany region.
The total amount of support is subject to the principle of degressivity based on the total area per action and crop group affected by the commitment (Tab. 2).
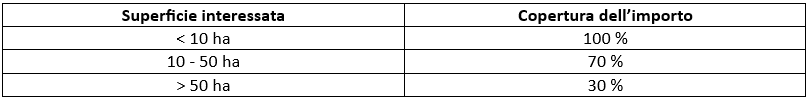
Tab.2: Principle of degressivity for the Tuscany region.
Cumulability:
ACA 24 is
cumulable with other interventions
, as summarized in Tab. 3.

Tab.3: Cumulability with other interventions.
Notice and application submission deadline:
The expected exit date for ACA 24 has been set by 11/30/2023 while the submission of applications for support must be submitted by 12/31/2023.
Selection Criteria:
Farms with a higher percentage of UAA in areas characterized by special environmental value (Natura2000 Sites, protected areas and sir), and areas characterized by environmental criticality such as Nitrate Vulnerable Zones will be favored in the selection, according to a scoring scale defined in each regional announcement.
Commitments to be met:
Commitment 1:
Accession to a digital service platform and DSS to collect and digitize farm data, treatment record, fertilization and irrigation inputs to support the farmer in making strategic choices.- Commitment 2: Use appropriate precision machines/equipment for the specific action:
– Action 1 – fertilizations to be carried out with appropriate precision machines capable of performing fertilization in the variable rate mode (VRT) through the reading of prescription maps;
– Action 2 – phytosanitary treatments should be carried out on the basis of forecasting models that estimate the probability of infections and infestations allowing timely intervention also with precision equipment. Weeding with precision equipment on the basis of farm mappings that allow control of weeds with localized interventions;
– Action 3 – irrigation on the basis of the soil water balance principle (e.g., FAO notebook No. 56) with special precision equipment capable of varying irrigation inputs according to soil characteristics of the soils and/or use of IOT sensors to measure soil moisture. - Commitment 3: the area requested with the application for support must be maintained throughout the duration of the commitment, with an overall tolerance in reduction of 20 percent. In addition, the area requested for premium with the payment application may involve variable plots, so it is possible to change with each year’s aid application the plots subject to commitment, subject to the number of hectares.
- Commitment 4: The beneficiary agrees to attend a training course and/or acquire counseling relevant to precision agriculture practices adoptable with the intervention.
Commitmentperiod:
Beneficiaries must meet, for a period of 5 years, previous commitments. The individual commitment annuality refers to the calendar year (January 1-December 31). The first year of commitment for Tuscany is 2024.
